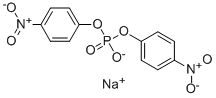
Bis(4-nitrophenyl)phosphate, sodium salt
CAS No. 4043-96-3
Bis(4-nitrophenyl)phosphate, sodium salt ( —— )
Catalog No. M23100 CAS No. 4043-96-3
Bis(4-nitrophenyl)phosphate, sodium salt is a PDE (Phosphodiesterase) substrate.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 66 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBis(4-nitrophenyl)phosphate, sodium salt
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBis(4-nitrophenyl)phosphate, sodium salt is a PDE (Phosphodiesterase) substrate.
-
DescriptionBis(4-nitrophenyl)phosphate, sodium salt is a PDE (Phosphodiesterase) substrate.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number4043-96-3
-
Formula Weight362.17
-
Molecular FormulaC12H8N2NaO8P
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESC1=CC(=CC=C1[N+](=O)[O-])OP(=O)([O-])OC2=CC=C(C=C2)[N+](=O)[O-].[Na+]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-g...
1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycerol is able to increase AChE activity by 35-40% at concentrations of 25 micrograms/ml in the parasite S. mansoni..
-
ADWX 1
Potent and selective KV1.3 channel blocker (IC50 values are 0.0019 and 0.65 nM for KV1.3 and KV1.1, respectively). Inhibits CD4+ CCR7- T cell activation. Ameliorates rat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, in a model for multiple sclerosis.
-
Fosfructose, sodium ...
D-Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate sodium salt hydrate is the intermediate in carbohydrate metabolism, including glycolysis and gluconeogenesis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


